We all have played games at least once in our lifetime more specifically in our childhood. Games, whether it be indoor or outdoor, give us a feeling of joy and plays a key role in relaxation by reducing stress.
In the current era, there is a rapid increase in playing indoor games, particularly video games. A majority of people irrespective of their age tend to play video games.
Due to advancements in games, there is a boost in performance and design. Modern games are designed with high-Quality graphics, which cannot be run singly handled by a PC, and the need for a graphic processing unit or ‘graphic card’ comes into demand.
Purchasing a graphic card isn’t as simple as it sounds. There are many factors to consider while buying one. One of the key factors to consider while purchasing a GPU is what type of Direct X would be supported.
Direct X is basically software with a collection of application programming interfaces (API) and allows data communication between a game and a graphic card. Direct X11 and 12 are the two latest types of Direct X supported by the latest graphic cards. Both the types have a difference between them which need to be considered.
One of the key differences between both types is that the Direct X11 manages to provide 19 Fps. Whereas, the Direct X12 is approximately 33% faster by managing 33 Fps.
This is just one distinction, there are many more facts and differences to know below. So, keep reading till the end as I will be covering all.
What is Direct X11?
Direct X11 or DirectX11 is a collection of application programming interfaces, which manage the relationship between the game graphic cards, multimedia hardware, sound card as well as the operating system. It was released on October 27, 2009, after its final update.
Direct X11 primarily runs on Windows 7, Windows 8, and Windows 10 operating systems. The Graphic Direct3D component of Direct X11 is primarily used by most graphics cards as it brings an enhanced and standardized feature set which makes it simpler for code authors for better-looking effects.
It supports tessellation and has improved multi-threading support which helps video game developers to develop games that can utilize multi-core processors better.
Direct X11 also comes with the feature that allows backward compatibility with the previous version of Direct X.
The decompression of even high texture images led to suboptimal images in the game and Direct X versions before Direct X11 didn’t support decompression. However, the Direct X11 was introduced with two texture decompression formats.
One is the BC6 format, which brings in compression of high dynamic texture, the compression brings a slight loss in the quality as it isn’t lossless. Second is the BC7 format it brings compression to low dynamic texture and works losslessly.
Since the Direct X 11 was launched, its four updates that are mentioned below were released:
- DirectX 11.1
- DirectX 11.2
- DirectX 11.X
- DirectX 11.3

How to check if Graphic Card would support Direct X11?
You can simply check if the graphic card supports Direct X 11 by following these steps:
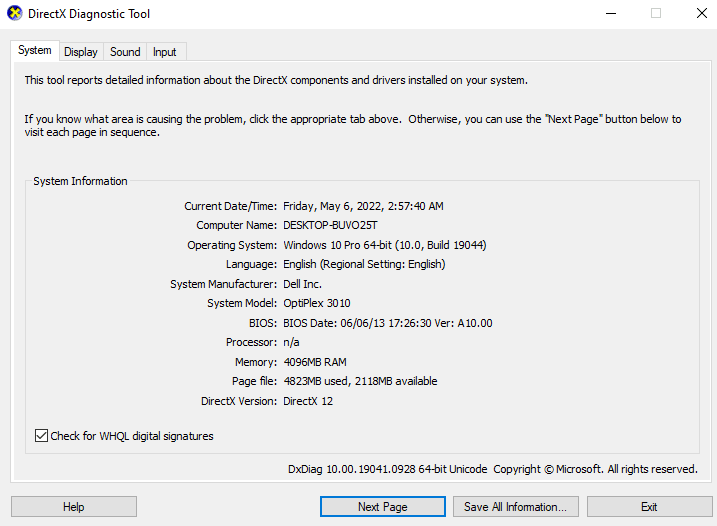
- Open the search bar in your Windows Start Menu and Search dxdiag.
- This will open the Direct X Diagnostic tool that will tell you quite a bit about your system.
- The supported version of Direct X will also be displaced somewhere at the bottom.
You also need to verify whether your graphic card itself supports Direct X 11 or not.
Keep in mind that, the Direct X 11 only supports runs on Windows 7, Windows 8, and Windows 10, if facing any problems do check your version of the operating system.
What is the Direct X12?
Launched on July 19, 2015, Direct X12 is a version of Direct X. Same as Direct X11, Direct X12 is a collection of application programming interfaces, which manages the relationship between the game graphic cards, multimedia hardware, and sound card, as well as the operating system.
It was officially launched for Windows 10 operating system. Direct X 12 enables developers to add astonishing graphic effects to Microsoft Windows-based PC games.
The primary feature of Direct X12 was the introduction of advanced low-level programming (API) for Direct3D 12. With Direct X12, developers were able to implement their own buffer and command list which would allow more efficient resource utilization.
D X12 mainly focuses on the dramatic increase in visual richness through the effective decrease in API-related CPU overhead.
The feature of multi-adapter support in Direct X12 allows developers to utilize multi GPUs on the system simultaneously. Previously the memory, state, and synchronization of OS applications were done on the behalf of developers which had a high risk of inefficient results. However, it is not the same with Direct X12 as it gives the application the ability to perform necessary synchronization and directly manage resources and state.
Direct X12 is supported in all Nvidia GPUs, Fermi, AMD’s GCN-based chips, and Intel’s Haswell. Same as any other software, Direct X12 is also installed. Don’t know the method to install it?
Watch this video to easily install it here:
Is Direct X12 good for gaming?
Yes! Direct X 12 is definitely great for gaming as it has improved CPU utilization and may improve average frame rate.
Most Direct X 11 and Direct X 12-based games only used 2 to 4 cores or various mechanics and some games are even limited to one.
It is not the same with Direct X 12-based games as it evenly distributes the load across all cores. Direct X 12 is most beneficial to boost the performance when Fortnite gamers need it the most.

Direct X11 vs Direct X12: What are the key differences?
Although both Direct X 11 and Direct X 12 have a couple of similarities, they are not the same. The differences between both these versions of Direct X outnumber their similarities.
| Direct X 11 | Direct X 12 | |
| Launched on | October 27, 2009 | July 19, 2015 |
| Runs on | Windows 7, Windows 8, and Windows 10 operating systems | Only Windows 10 operating system |
| Features | Tessellation, multi-threading support, allows backward compatibility with previous versions, two texture decompression | low-level programming (API) for Direct3D 12, multi-adapter support, provides applications the ability to perform necessary synchronization and directly manage resources and state |
Direct X12 vs. Direct X11: Which is better?
Both, the collection of (APIs), Direct X and Direct X12 have their unique features and characteristics which benefit the user experience in a great way.
When comparing both the versions, Direct X12 is way better than the Direct X11.
When it comes to power saving, Direct X 12 saves 50% of CPU power than Direct X 11. Not does Direct X 12 only saves power, but it can also yield 50% better FPS performance. The Direct X 12 is approximately 33% faster by managing 33 Fps.
Direct X 12 also has improved CPU utilization and it evenly distributes the load across all cores, making Multi-core CPUs more relevant for gamers.
Conclusion
Direct X11 and Direct X12 are two versions of Direct X. Although both these versions seem to be similar in reality both are not the same in terms of their function and the operating systems in which they are run.
Whether you choose to use Direct X 11 or Direct X 12, it is first and foremost important to consider that your system and its operating system support it.
Both Direct X11 and Direct X12 are not just great in their features but also provide the best user experience within their capability.

