With primary elections starting soon, many people are turning to the internet to ask a very important question: “Is there a reason for mayors to exist?” And the short answer is: “Yes, there is.“
While they are often mistaken for the other, the roles, responsibilities, and necessary qualifications for a governor could not be more different than a mayor.
Basic Hierarchy of the Government
A government includes a group of people who make and control decisions made for a country, state, and city.
The U.S. government structure can be divided into three basic categories, which ensure that no individual or group is given too much power.
We’ve drawn the following table to help you visualize the current structure:
| Executive Branch | Legislative Branch | Judicial Branch | |
| Federal Level | President | U.S. Senators and Representatives | Federal Judges |
| State Level | Governor | State Senators and Assembly members | State Judges |
| Local Level | Mayor | City Council members | Trial Judges |
The Role of Branches:
- Executive Branch. This branch is responsible for enforcing the law. This includes the President, Vice-President, Cabinet, Executive Departments, independent agencies, and other boards and committees.
- Legislative Branch. This branch is responsible for accepting or rejecting presidential nominations for heads of federal agencies, federal judges, and the Supreme Court and has the authority to declare war. It is also responsible for drafting new laws. This comprises the Congress and special agencies supporting the House.
- Judicial Branch. It interprets the meaning of laws and decides if laws violate the constitution on a case-by-case basis. It consists of the Supreme Court and other federal courts.
What is a Governor?

According to the Oxford Dictionary, the governor is chosen to be in charge of the government of a state in the U.S. Governors have power over the executive and judiciary branches at a state level and are subservient to the President.
The 8 primary duties of a governor:
- Signing bills into federal law.
- Organizing sessions for the state.
- Delivering a “State of the State” address, which involves reporting the conditions of their state to the state legislature.
- Management of both natural and man-made crises.
- Clemency – the power to pardon a criminal or reduce their sentence. Pardoning a criminal means erasing their criminal record and restoring their basic rights (such as the right to vote).
- Intergovernmental Liaison – governors of one state must pay attention to the actions and their potential consequences on other states. In addition, they represent the needs of their state to the national government and must often work with other states to address common political, moral, and financial problems.
- Serving as Commander-in-Chief of the state’s National Guard and military forces.
- Hosts foreign ambassadors and dignitaries to promote their state and develop goodwill.
A governor exercises a large amount of power and authority, which can be compared to the power exercised by the President, albeit on a smaller scale. They are even provided with a state-administered residence, known as the “Governor’s Mansion”.
It should be noted that a good relationship between the State Governors and the President is vital for the successful implementation of new policies and laws.
Taking President Trump as an example, multiple conflicts between the President and the Governors served to weaken the constitutional foundation of America, leading to disagreements in political, social, economic, and even healthcare policies.
Important Qualifications Required to Become a Governor
The qualifications necessary to become a governor vary from state to state. There are three similar requirements:
- Be at least 30 years old on the day of inauguration.
- Has been an American citizen for at least 15 years.
- Has been a resident of that state for anywhere between 5 to 15 years (this is dependent on the state).
Candidates with prior political experience are preferred over those with no experience.
Why should you care who the Governor is?
Well, it’s because you have the power to choose. The governor represents your state to the entire country, if not the entire world.
Choosing someone who is politically weak and/or corrupt can have devastating consequences for you. Some governors charged with corruption include:
- Rod Blagojevich, the 40th Governor of Illinois, was found guilty of attempting to sell President Obama’s former U.S Senate seat in 2011 and is currently serving a 14-year prison sentence.
- Don Siegelman, the 51st Governor of Alabama, was convicted on federal felony corruption charges in 2006 and was immediately sentenced to seven years in federal prison.
- Most recently, Bob McDonnell, the 71st Governor of Virginia, faced federal corruption charges for receiving improper gifts and loans from a Virginia businessman. He was convicted on most counts by a federal jury in 2014 and was sentenced to two years in federal prison.
Approximately 1 in every 4 Americans believes that their government is corrupt, while a large majority agree that there is little action taken to counter corruption. Therefore, it is vital for voters to be careful about who they give their valuable votes to, as their decision decides the fate of their home state, and is an opportunity for them to take charge of their future.
How is a Mayor different from a Governor?

A mayor is an official elected or appointed to act as chief executive or nominal head of a city or a town. Currently, there are approximately 1,400 mayors in the United States.
Unlike a governor, a mayor oversees the main departments of a city (or municipality), including the police, fire, education, housing and transportation departments. They have additional roles based on the city’s power structure, which is set up by the city’s charter or statutory laws.
Common Responsibilities of a Mayor
While not as media-focused as compared to national and state governments, the local governments run by mayors play an important role in the everyday lives of American citizens.
According to the National League of Cities (NLC), common responsibilities of a mayor include:
- Serving on the city council.
- Voting in council meetings.
- Appointing council members to serve on committees or chairs.
- Assigning citizens to serve on commissions or advisory boards.
- Developing the annual budget; getting the annual budget prepared by the city manager or chief administrator.
- Prepare an annual report for the council.
Additional responsibilities of a mayor include:
- Approving press releases, speaking with journalists, leading press conferences, and completing other media availability tasks.
- Representation of the town at meetings with official government entities.
- Assigning staff to government positions like city secretary, city attorney, and other unelected positions.
- Attending public events in an official capacity.

Strong Mayor vs Weak Mayor
A mayor can be classified as either “strong” or “weak”, which has less to do with effectiveness and more to do with the level of political and legislative power bestowed on them.
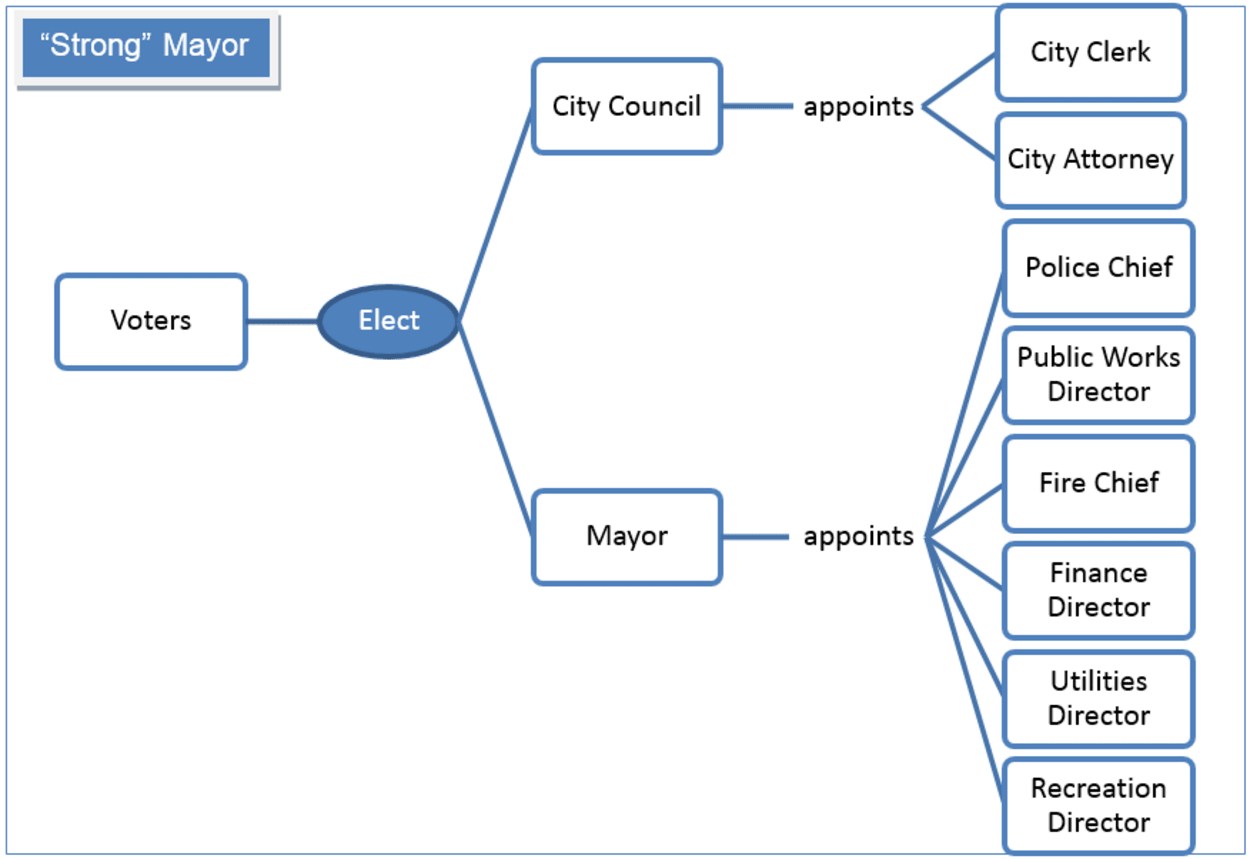
Strong Mayor
The citizens directly elect a “strong” mayor and are in a mayor-council form of government.
A strong mayor has large legislative powers and is able to dismiss council suggestions and recommendations. The mayor designs and administers the city’s annual budget and has enough power to appoint/dismiss department heads without council approval or public input.
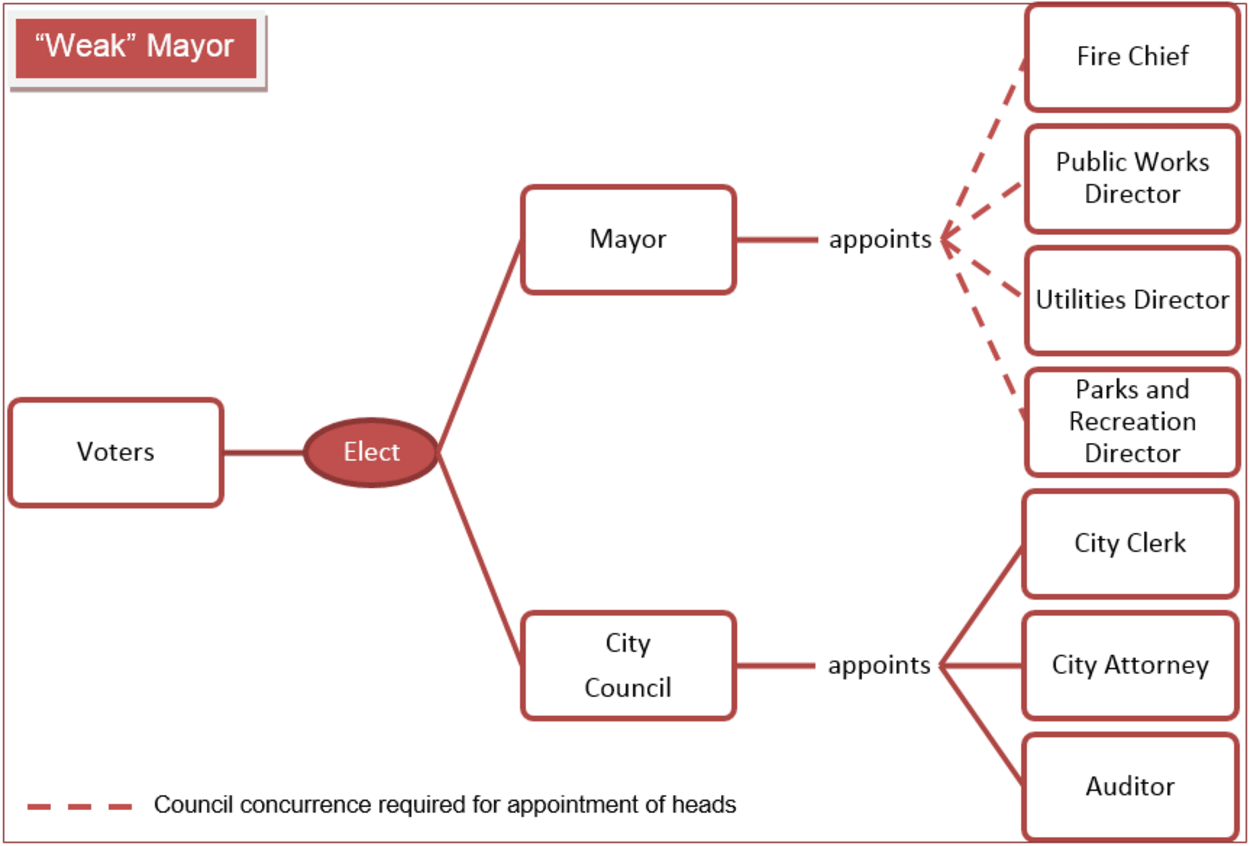
Weak Mayor
On the other hand, a “weak” mayor has virtually no authority outside the council and is unable to veto council votes.
They cannot appoint or dismiss department heads and have no influence over the city. The council handles day-to-day tasks, with the mayor serving as a ceremonial figure. Some administrative boards and commissions may operate independently from the city government.
In this case, the mayor is appointed by the city council on a rotatory basis, and this method is popular in many small cities.
Interestingly enough, studies claim that a council-manager (weak mayor) system is more effective than a mayor-council (strong mayor) system.
This is because a strong mayor would be primarily concerned with electoral politics, while a city manager (or weak mayor) would be more attentive to the improvement of the city, along with the expectations of their fellow City Council members.
Mandatory Requirements to Run as a Mayor
In order to run as a mayor, a person must fulfill the following requirements:
- The individual must have resided in the city for at least a year prior to the election or appointment thereto and, if elected, must receive a plurality of votes cast for that office in the entire city.
- It is mandatory for the mayor to stay within the city during the person’s office term, or the office shall remain vacant..
- They must not have been sentenced for fraudulent violations of primary or election laws, malfeasance in office, or felony involvement in moral turpitude.
In Summary
- Knowing the differences between governors and mayors is vital for civic engagement.
- The U.S. government has three main branches. They are federal, state, and local.
- Governors oversee states. They handle tasks from signing bills to crisis management.
- Governor qualifications include age, U.S. citizenship, and state residency.
- Mayors manage cities, overseeing police, fire, education, and transportation.
- Mayors can be strong or weak. They impact legislative and administrative powers.
- The choice of governor or mayor affects citizens’ well-being. It urges voters to stay vigilant.
- Understanding officials’ duties and being aware of corruption risks is crucial. It helps citizens make informed election choices.
Other Articles:
- The Difference Between Imax and a Regular Theater
- Salespeople vs Marketer
- What is the Difference Between the Project Manager and a Project Management Officer
Click here to know how different governors and mayors are through a web story.

