PCI stands for “Peripheral Component Interconnect,” and PCLe (PCL Express) is a popular computer bus standard used to connect peripheral devices such as graphics cards, network cards, and storage devices to the motherboard of a computer.
PCLe comes in different versions; 2.0 and 3.0. Out of many differences, the main ones are the data transfer capability, number of lanes, and action speed.
With the release of PCIe 3.0, there was an increase in the speed and bandwidth compared to PCIe 2.0, the data transfer capability is more in PCLe 3.0.
In this article, we will explore the differences between PCIe 3.0 and 2.0 in detail and answer some of the frequently asked questions. So, let’s get started!
What Is PCI Express 2.0?
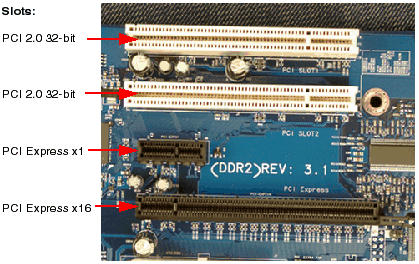
PCI Express 2.0 was introduced in January 2007, and it’s the second version of the PCI Express standard.
PCIe 2.0 supports a maximum speed of 5 Gbps per lane, which means that a PCIe 2.0 x16 slot can transfer data at a maximum speed of 80 Gbps.
PCIe 2.0 has also added new features, such as improved power management, better error handling, and the ability to scale the number of lanes dynamically.
What Is PCI Express 3.0?
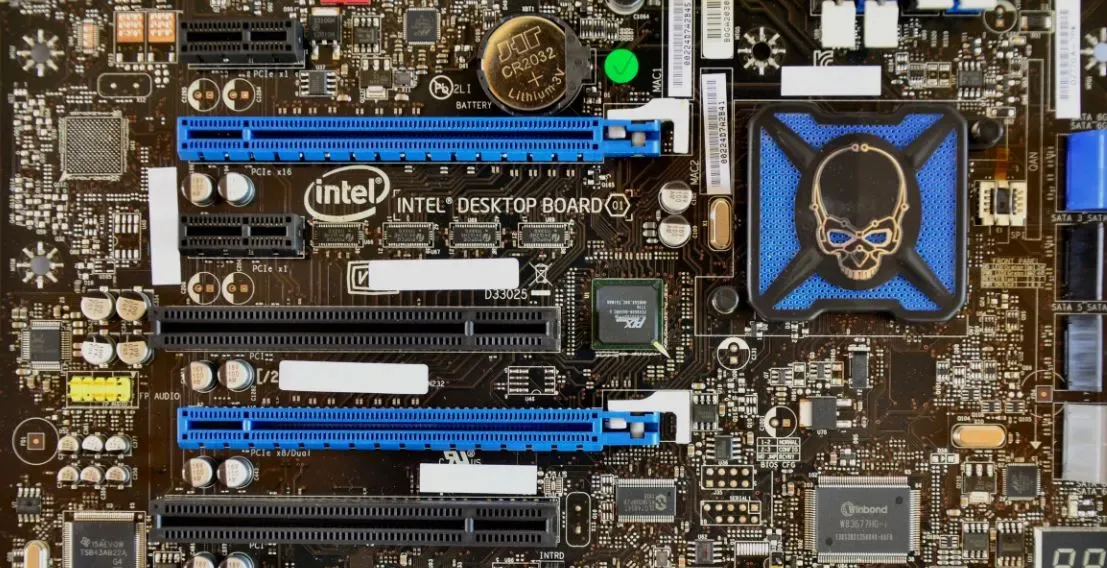
PCI Express 3.0 was introduced in November 2010, and it’s the third version of the PCI Express standard.
PCIe 3.0 supports a maximum speed of 8 Gbps per lane, which means that a PCIe 3.0 x16 slot can transfer data at a maximum speed of 128 Gbps.
PCIe 3.0 also includes several new features, such as the use of multiple lanes to increase bandwidth, improved power management, and support for larger packets.
Discussing The Differences Between PCLe 2.0 And 3.0
Bandwidth
The capacity of a network to transfer information within a given distance is called its, ‘Bandwidth.’
One of the primary differences between PCIe 3.0 and 2.0 is the increase in bandwidth.
PCIe 2.0 has a maximum bandwidth of 500 MB/s per lane, while PCIe 3.0 has a maximum bandwidth of 1 GB/s per lane.
This increase in bandwidth means that PCIe 3.0 can transfer data at a faster rate than PCIe 2.0.
Number of Lanes
Another significant difference between PCIe 3.0 and 2.0 is the number of lanes.
PCIe 2.0 has a maximum of 16 lanes, while PCIe 3.0 can support up to 32 lanes. More lanes mean that there is more bandwidth available, which can lead to better performance.
However, it is important to note that not all devices require more lanes to perform better.
Compatibility
Because PCIe 3.0 and PCIe 2.0 are backward compatible, a PCIe 3.0 device can be utilized in a PCIe 2.0 slot and vice versa.
Backward compatibility refers to the hardware or software versions that have the ability to connect with older interfaces of their versions.
However, when a PCIe 3.0 device is used in a PCIe 2.0 slot, the device will operate at the speed of the PCIe 2.0 slot. This means that the device will not be able to achieve its full potential performance.
Whereas if we connect a 2.0 slot in PCLe 3.0 version, it will operate with the speed of the 3.0 version, which will enhance performance.
Power Management
Another difference between PCIe 3.0 and 2.0 is power management.
PCIe 3.0 includes improved power management features, such as the use of the L1 sub-state to save power when the device is idle.
This means that PCIe 3.0 devices can save more power when compared to PCIe 2.0 devices.
Error Handling
PCIe 3.0 includes improved error handling features, which help to reduce errors during data transfer.
For example, PCIe 3.0 includes an advanced error reporting mechanism that can detect and correct errors in real-time.
This means that PCIe 3.0 devices are less likely to experience errors during data transfer than PCLe 2.0.
Additional qualities
There are some additional qualities that were introduced in the PCLe 3.0 version, as an improvement of the older generation versions.
Backchannel equalization in PCle 3.0 version was brought to reduce the risks of channel loss due to the silicon components. Moreover, encoding systems contributed to the speed increase of upcoming generations.
Latency
Latency is the time it takes for data to travel from one device to another.
PCIe 3.0 has lower latency than PCIe 2.0. This is because PCIe 3.0 includes features such as faster link initialization, improved clocking, and reduced overhead.
Cost
As with any new technology, PCIe 3.0 is more expensive than PCIe 2.0. This is because PCIe 3.0 requires more advanced components, such as high-speed signal processing chips and improved circuit boards.
However, as the technology becomes more widespread and more versions come out, the cost of PCIe 3.0 devices will decrease.
| Specification | PCIe 2.0 | PCIe 3.0 |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Bandwidth | 500 MB/s per lane | 1 GB/s per lane |
| Maximum Lanes Supported | Up to 16 lanes | Up to 32 lanes |
| Power Management | No | Yes |
| Error Handling | No | Yes |
| Additional qualities | none | Backchannel equalization, enhanced encoding, etc. |
| Latency | Higher | Lower |
| Cost | Less expensive | More expensive |
Real-World Performance
While PCIe 3.0 offers better specifications than PCIe 2.0, the real-world performance difference may not be as significant.
This is because many devices do not require the full bandwidth offered by PCIe 3.0.
For example, a network card may only require a few hundred megabytes per second, which can be easily achieved with a PCIe 2.0 connection.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Is PCIe 3.0 backward compatible with PCIe 2.0?
Yes, PCIe 3.0 is backward compatible with PCIe 2.0, which means that a PCIe 3.0 device can be used in a PCIe 2.0 slot, and vice versa. However, when a PCIe 3.0 device is used in a PCIe 2.0 slot, the device will operate at the speed of the PCIe 2.0 slot.
What is the maximum bandwidth of PCIe 3.0 and 2.0?
PCIe 3.0 has a maximum bandwidth of 1 GB/s per lane, while PCIe 2.0 has a maximum bandwidth of 500 MB/s per lane.
What is the maximum number of lanes supported by PCIe 3.0 and 2.0?
PCIe 3.0 can support up to 32 lanes, while PCIe 2.0 can support up to 16 lanes.
Is PCIe 3.0 more expensive than PCIe 2.0? Yes, PCIe 3.0 is more expensive than PCIe 2.0. This is because PCIe 3.0 requires more advanced components, such as high-speed signal processing chips and improved circuit boards.
Conclusion
PCIe 3.0 offers several improvements over PCIe 2.0, including increased bandwidth, improved power management, better error handling, and lower latency.
However, the real-world performance difference may not be as significant as the specification difference.
Additionally, not all devices require the full bandwidth offered by PCIe 3.0, and PCIe 2.0 is still a reliable and widely used technology.
Ultimately, the choice between PCIe 3.0 and 2.0 will depend on the specific requirements of the device and the available budget.

