It’s time to break down the shades. Have you ever heard someone call your tan skin “brown” or your dark skin “black”?
We all confuse skin shades with each other. For instance, we take brown skin the same as dark skin.
Brown skin is a mix of dark and light skin color, whereas dark skin color is more of a black shade due to high melanin levels.
In this article, we’ll uncover what lies beneath the surface and explore the differences between brown and dark skin.
We’ll examine how melanin plays a role in our individual colors, why we can’t simply divide our complexions into neat categories, and how we are more alike than different. So grab a cup of tea, open your mind, and let’s get started!
What Is Brown Skin And Dark Skin?
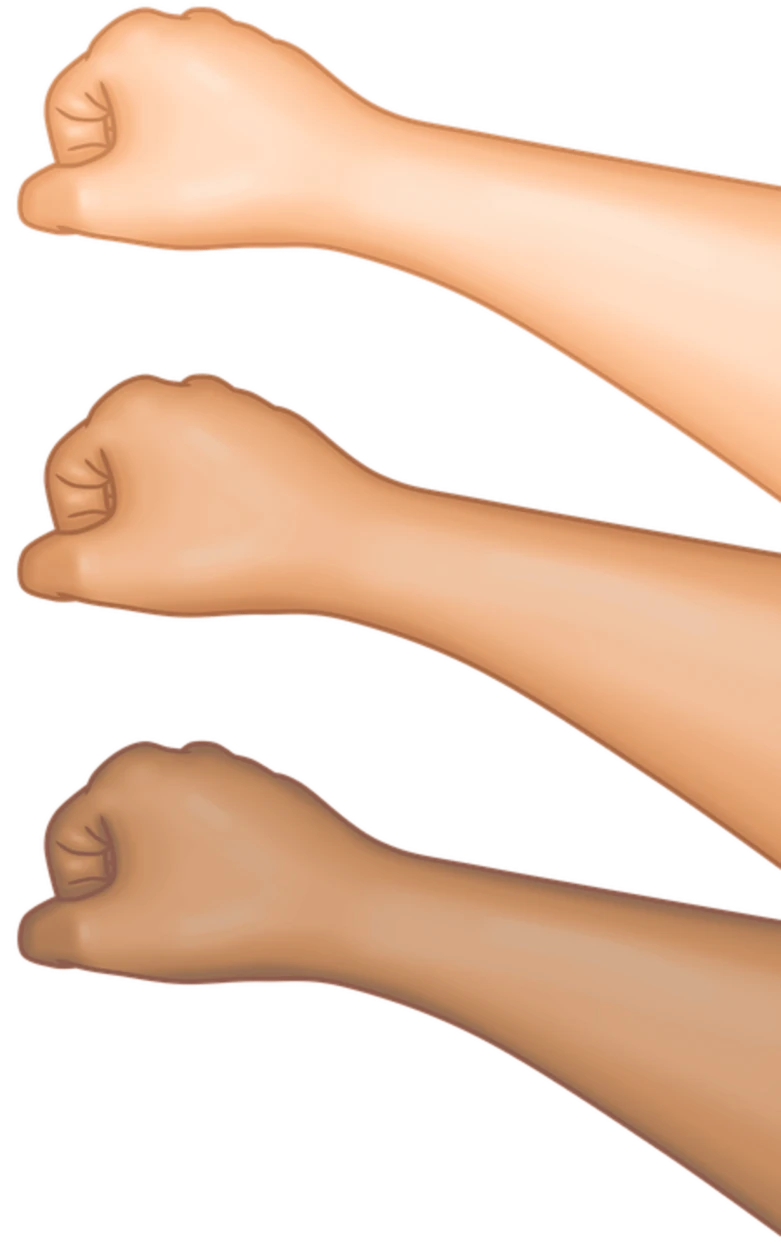
People of color can come in many different shades and complexions. From fair to dark, different levels of melanin present in the skin can range from light brown to dark brown and even black.
But what is the difference between brown and dark skin?
At its core, brown skin is generally a lighter complexion than dark skin. Brown skin has a higher melanin level than lighter complexions, but less than darker complexions like black.
It can range in tones from light tan to golden tan, while dark skin covers more deeply pigmented tones like deep brown and muted black.
Additionally, the primary distinction between brown and dark skin lies in the specific pigment cells that are responsible for each one.
Darker skins (like ebony or jet black) contain large quantities of the pigment melanin—a chemical responsible for controlling pigment production in the body.
Why The Difference?
It’s important to understand the differences between brown and dark skin but it’s also crucial to know why these differences exist in the first place. To properly answer this, we have to travel all the way back to genetics.
Humans all share the same basic set of DNA, but not everyone looks the same.
The reason? Alleles.
Alleles are genetic variants of a species that allow for physical variations from person to person. For example, different alleles can cause a person’s skin color to range from extremely light to very dark.
The most common allele associated with lighter skin color is labeled MC1R and is found in people with fair complexions, while darker complexions are associated with a different type of allele called KITLG which is responsible for melanin production.
The latter helps protect against harmful UV rays for those living closer to the equator.
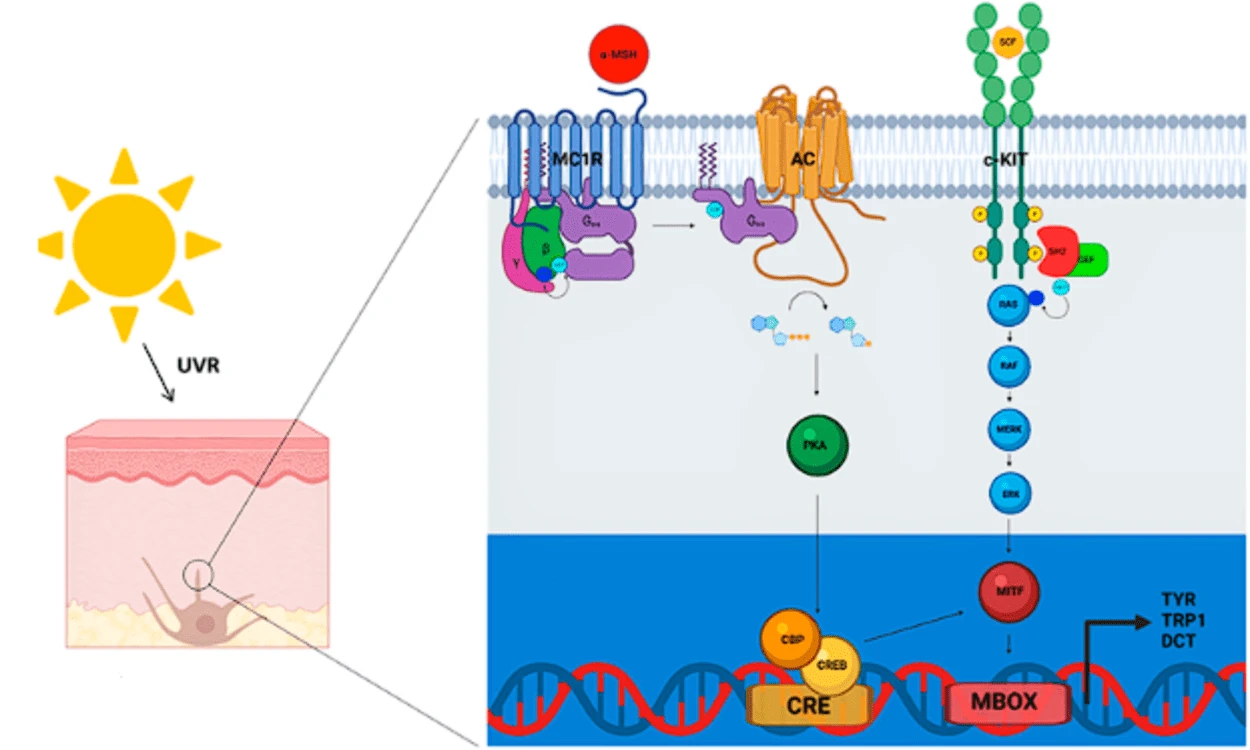
These variations in alleles give rise to different shades of brown and dark skin, making it important for everyone across the spectrum to have access to products that fully accommodate their unique needs like skincare specifically tailored for brown or dark skin tones.
Cultural Issues In Understanding Skin Tone
There is more to consider regarding skin color than merely a technical comprehension of it.
The terms “brown” and “dark” have distinct connotations for different individuals. For example, “brown” may be used to refer to all persons of color, whereas “dark” may be used to describe someone who is darker than others.
When discussing skin tones, this misunderstanding can cause confusion, but the best course of action is to approach talks with empathy and pay attention to the words each person uses.
Afro-Caribbean and African American individuals can have a variety of skin tones within their own communities, sometimes even having lighter skin than other people of color from various origins.
Moreover, tone within one race doesn’t necessarily stay within that race’s bounds. It’s critical to keep in mind that each person is special.
Different Types Of Brown And Dark Skin Tones
Understanding the many hues and variations of these colors can be useful when discussing skin tones that are referred to as brown or dark.
While precise classifications might be difficult to come by, the three basic groups of skin tones are ebony, olive, and golden brown.
Skin Tone Ebony

The deepest shade of brown skin is called ebony, and both Africans and African Americans frequently have it.
Deep black to light brown are only a few of the various tones of this color. Ebony skin tones vary from person to person; there is no one-size-fits-all color for this complexion.
Olive complexion
Olive skin tones are a lighter version of ebony than they are of golden brown.
It’s frequently referred to as “yellowish-brown” or “greenish-brown.” Individuals with olive skin tones typically tan easily in the sun because they have higher melanin levels than people with golden brown skin tones.
Golden Brown
Compared to ebony or olive skin tones, golden brown is a pale shade of brown that has a tendency to be warmer and more yellow in color.
It is sometimes referred to as having a caramel or honey complexion. Lighter golden brown skin tones tend to tan more readily in the sun without burning too rapidly.
Highlighting Positives Of Skin Color Variance
It’s crucial to keep in mind that everyone has beautiful skin, regardless of skin tone. This has a lot of advantages, particularly in terms of representation.
For instance, those with darker skin tones are frequently excluded or rendered invisible in the media. Everyone benefits from seeing a variety of skin tones represented, as it makes them feel celebrated and seen.
For people with dark skin, who can now see people who resemble them in everything from movies and television shows to magazines and commercials, it’s also reassuring.
Also, there are more chances today for people with darker skin to appreciate their beauty and draw attention to their distinctive qualities.
There are so many ways for people with brown or dark complexion to express themselves, from choosing the ideal foundation shade match to discovering a natural beauty routine that suits them best.
So, take a moment to appreciate the broad range of skin tones this earth has to offer; each and every one of us is lovely!
Overcoming Colorism Through Education And Respect
Though colorism has deep roots, it is not insurmountable. We may begin to shift away from valuing one skin tone above the other by educating ourselves and others on the genuine intricacies of different skin tones.
Education
Instead of perpetuating unfavorable stereotypes, it’s critical to attempt to normalize various skin tones. This entails having more open conversations regarding skin tone disparities and educating people about them.
Moreover, make an effort to understand that beauty exists in many shades, from light brown to the darkest black.
Respect
The key to overcoming colorism is respecting all skin tones and realizing that no color or hue is superior to another.
Congratulate and show admiration for those who have skin tones that differ from your own. When you embrace everyone’s beauty, you may fight to eradicate the stereotypes that are frequently attached to those with darker skin tones.
We may begin to build an environment where colorism no longer permeates modern society by educating ourselves and showing respect for each person’s unique beauty.
Celebrating diversity and promoting inclusivity
The most crucial thing when it comes to representing people with brown or dark complexion is to celebrate diversity and advance inclusivity. Each of these skin tones must be accurately and impartially represented.
Showing Appreciation
It’s crucial to express admiration for dark skin tones and all colors of brown. Everyone should be confident in their own complexion, and no one should feel inferior or ridiculed because of their skin tone.
Embracing Diversity
Instead of being perceived as labels or groups of individuals, people with a dark complexion and those with brown skin should both be appreciated.
Because every person has a different shade, it’s appreciated to treat each person as an individual rather than a collection of people who are labeled the same.

Instead of contrasting different colors or making snap judgments about people based solely on their skin tone, we may all work together to appreciate the beauty in each person’s individual skin tone.
We can overcome our prejudices regarding skin color and begin advocating for true inclusivity and acceptance of all hues across the spectrum when we learn to value each person for their unique beauty.
Factors That Contribute To Skin Color
When it comes to skin color, there are a few factors that play a role in it. It’s been said many times that beauty comes in all shapes and colors and that’s very true when it comes to skin, too.
Here are some of the main determining factors of skin color:
| Genetics | Melanin is the pigment responsible for giving human skin, hair, and eyes their color. Melanin production can vary based on the amount of exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light. People who live closer to the equator tend to have darker skins because they receive more intense UV radiation than people closer to the poles do. |
| Melanin production | Melanin is the pigment responsible for giving human skin, hair, and eyes their color. Melanin production can vary based on the amount of exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light. People who live closer to the equator tend to have darker skin because they receive more intense UV radiation than people closer to the poles do. |
| Sun exposure | Being exposed to direct sunlight can also affect your skin tone, as this kind of exposure affects melanin production leading to changes in your complexion over time. The UVA rays from sunlight cause premature aging and wrinkles, while UVB rays cause sunburn or darkening of the skin through melanin production and tanning. |
FAQs
Is there a lower limit for dark skin?
No, there is no lower limit for dark skin. While people with light brown skin can appear similar to those with fair skin, it’s important to note that darker-skinned people typically experience greater stigma due to the long history of colorism and racism in the world.
How can I tell whether someone has brown or dark skin?
The best way to tell whether someone has brown or dark skin is by looking closely at their complexion.
Darker-skinned individuals often have deeper, richer shades as opposed to those with lighter complexions. However, it’s important to remember that everyone’s shade is unique and should be respected regardless of variations in hue or intensity.
Is skin color related to race?
In many cases, yes. Skin color is often used as an indicator of racial identity; however, it’s important to remember that race and ethnicity are socially constructed categories and should not be used as a means of determining someone’s identity or character.
Conclusion
- Understanding the differences between brown and dark skin tones is key to embracing and celebrating diversity.
- It’s a reminder to appreciate the tone, complexion, and unique beauty of all skin colors—from the lightest of light to the darkest of the dark.
- Brown skin is a mix of dark and light skin color, whereas dark skin color is more of a black shade due to high melanin levels.
- It doesn’t matter how light or dark our skin is. We’re all related and part of the same human family.
- Skin color can be determined on the basis of heredity, UV exposure, diet, etc.

