Science has done many wonders in the past, and the world is doing in the present and is getting ready for the future. The word “science” has been taken from the Latin word “Scientia”, which means knowledge; this knowledge is based on hypotheses, observations, and experiments of universal science.
As in chemistry, the movement of ions is discussed, which requires different types of cells. The device that transforms chemical energy into electrical energy or vice versa by a redox reaction is known as an electrochemical cell. The electrochemical cells are electrolytic and galvanic (voltaic cells).
An electrolytic cell is a cell that consists of positive and negative poles known as an anode and cathode. On the other hand, a galvanic cell is defined as an electrochemical cell that is used to convert the chemical energy of spontaneous redox reactions into electrical energy.
The electrolytic cell is used for the process of electrolysis, which is a process of current passing through an electrolyte. Due to this, the migration of negative and positive ions toward the anode and cathode takes place.
A galvanic cell, also called a voltaic cell, is an electrochemical cell that uses chemical reactions to generate electrical power.
Both of these cells are still as useful as they were at the time of their invention, which means they have not lost their value in today’s revolutionist society.
The importance and differences between galvanic cells, or voltaic cells, and electrolytic cells are discussed extensively in this article.
Electrolytic Cell: How Does it Work?
An electrolytic device that employs electrical energy to induce a non-spontaneous redox reaction is known as an electrolytic cell. Certain chemicals can be electrolyzed using electrolytic cells, which are then called electrochemical cells.

For instance, water can be electrolyzed to create gaseous oxygen and gaseous hydrogen with the use of an electrolytic cell. This is accomplished by leveraging the flow of electrons (into the reaction environment) to break through the non-spontaneous redox reaction’s activation energy barrier.
The main parts of electrolytic cells are:
- A cathode (negative charge)
- An anode (positive charge)
- An electrolyte
The dissociated positive ions in the electrolyte are drawn to the cathode of the electrolytic cell when an external electric current flows through it. This causes the positively charged ions to settle on the cathode.
The positively charged anode is approached by the negatively charged ions at the same time.
What Is A Galvanic Cell And How Does It Work?
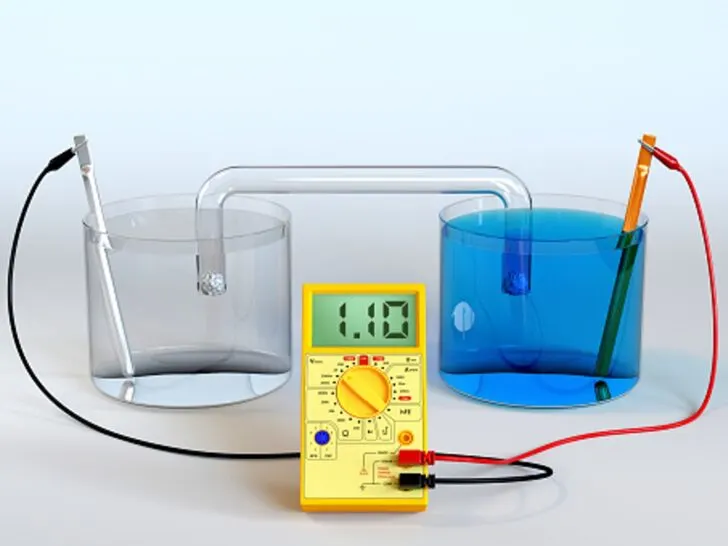
A galvanic or voltaic cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy through random redox reactions. A galvanic cell is an electrochemical device that creates electricity through chemical operations.
The common apparatus consists of two different electrodes.
One is made up of copper and the other is zinc; both are placed in separate beakers containing their respective metal ions in solution, which are connected by a salt bridge and are separated by a porous membrane.
The purpose of the production of electrolytic cells is to convert electrical energy into chemical energy by exposing the electrolyte to two metals charged and connected to a battery, respectively.
The cause of the production of galvanic cells or voltaic cells is that they are capable of converting chemical energy into electrical energy, which is required for work purposes.
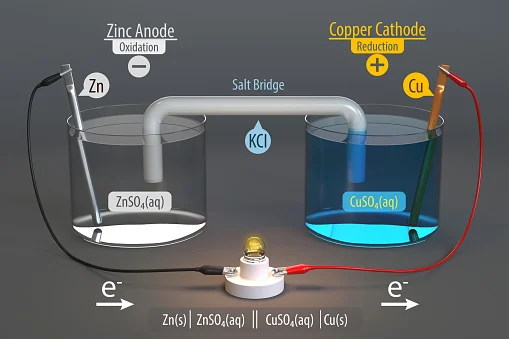
Distinguishing Facts Between Galvanic and Electrolytic Cells
Electrolytic cells and galvanic cells have some contrasting features discussed in the table below.
| Features | Electrolytic Cell | Galvanic or Voltaic Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Production | The electrolytic cell uses a vessel that is filled with electrolytes and there are two electrodes dipped in it which are connected to the battery respectively making them anode and cathode. | The galvanic cell or voltaic cell is produced when two beakers filled with electrolytes and two electrodes are dipped in this solution. These beakers are connected by a salt bridge and both electrodes are connected by a battery respectively. |
| Energy | The electrolytic cell converts electrical energy into chemical energy through a redox reaction which is spontaneous and is in charge of the production of electrical energy. | A galvanic or voltaic cell is a cell that transforms chemical energy into electrical energy through a redox reaction that is very useful for work purposes. |
| Source of energy | An electrolytic cell requires an external source of energy to function. a battery is connected to both electrodes that start the working of the electrolytic cell. | The galvanic or voltaic cell does not require any external source of energy as it produces its energy. |
| Charges | The electrolytic cell contains negatively charged anodes and positively charged cathodes. | Galvanic cell or voltaic cell contains positively charged anode and negatively charged cathodes. |
| Reactions | Electrolytic cells use spontaneous reactions to produce chemical energy. It converts electrical energy into chemical energy. | Galvanic or voltaic cells use non-spontaneous reactions to produce electrical energy. it converts chemical energy into electrical energy required for work. |
Practical Applications of the Electrolytic Cell
The electrolytic cell has played an important role for itself in today’s society and is used in mass numbers. The practicality and importance of electrolytic cells are listed below:
- It is used to prepare sodium metal from molten sodium chloride using the down cell.
- It is used to obtain chlorine gas and prepare caustic soda (NaOH) from aqueous sodium chloride by Nelson cell.
- It is used to extract aluminium metal.
- It is used in the electro-refining of copper.
- Electrolytic cells are used for electroplating metals.
- The electrolytic cell is used to produce oxygen gas and hydrogen gas from water by delivering it through electrolysis.
Practical Applications of Galvanic or Voltaic Cells
Galvanic or voltaic cells are an important invention for today’s world and are used far and wide by mankind. Electricity is a basic necessity of modern life and its production is one of the most difficult processes, yet we have so many ways to produce electricity.
Galvanic or voltaic cells are one of the earliest methods of generating electricity. It still possesses significant importance among the new and modern methods of producing electricity.
- The process of galvanic cells has many types and is impacting human life in many ways. Dry cells or batteries, which we commonly use in our everyday lives, power our flashlights, TV controls, gaming controllers, and so many other things.
- The lead-storage battery is also an everyday example of a galvanic cell. The function of a lead-storage battery is to generate electricity when the main power supply is off. It is commonly used as a backup in houses and workplaces.
- Fuel cells are widely used in industries as their backup needs to be bigger. These are used when the electricity is out and machinery has to work.
Conclusion
- Electrolytic cells use electricity for non-spontaneous reactions.
- Galvanic cells convert chemical energy to electricity. Electrolytic cells need external power. While galvanic cells generate their own.
- Electrolytic cells have negatively charged cathodes, and galvanic cells have positively charged ones.
- Electrolytic cells extract metals, electroplate, and produce gases. Galvanic cells power batteries and fuel cells.
- Both cell types are important in modern life. And they are widely studied.
- Understanding their differences is important. It aids in scientific progress.
- The use of both cells is now famous and familiar in the entire world. This remarkable invention is now a part of the youth’s syllabus and is taught to every child nowadays.
- The method that undergoes the production of both electrolytic and galvanic cells is simple. And it is easily accessible to the common man.

