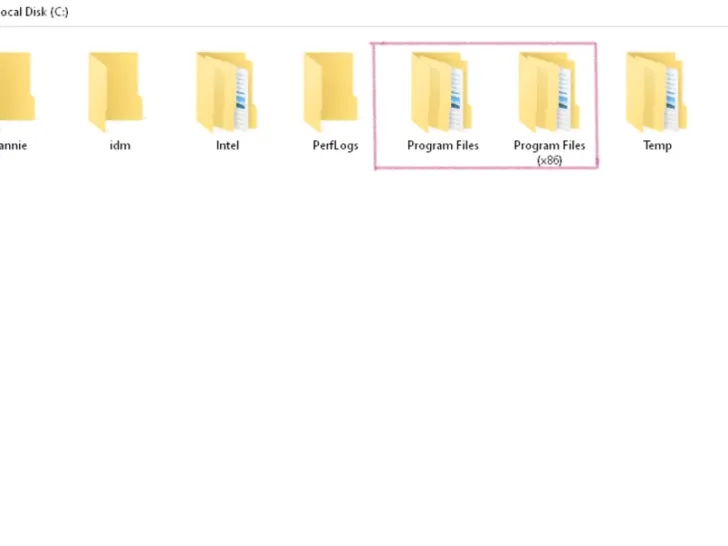
Have you ever wondered what’s the difference between program files and program files (x86) on C Drive? Well, here’s a short answer:
These are two file types on a C drive where data of different sizes are installed. The main folder where applications of 64-bit size are installed is ‘Program Files’. While 32-bit size compatible applications land in Program Files (x86).
As far as Windows is concerned, there are two versions, 32-bit and 64-bit.
Program files are the most important files on your computer. They contain your programs, applications, and settings. They are often referred to as “.exe” files on Windows computers and “.dmg” files on Mac (Apple) computers, although these terms are used by different operating systems.
Throughout this article, I’ll discuss the use of these program files in detail and address your different queries.
So, let’s explore these digital details…
Program Files
This is the folder that is available on both 32-bit and 64-bit versions of the Windows Operating Systems. On a 32-bit compatible Windows Operating System, files and applications of the 32-bit size will be installed.
Whereas a 64-bit operating system stores files of 64-bit in the folder named ‘Program Files’. It’s important to note that you can’t store files that are larger than 32-bit on a 32-bit variant of the Windows Operating System.
What Are Program Files (x86)?
Not many people know how many bits their computer has. In Windows, there are usually two variants: 32-bit and 64-bit. When installing files and software, it’s really important to unveil this information.
The best way to do this is to check whether there are two program files in the C drive, including Program Files (x86). If your hard drive has this folder, it means your computer is 64-bit.
Since the 64-bit variant of the Windows OS installs 32-bit files separately, this folder is created on a C drive. The chances of a conflict are high if you download two different versions of the same application, 32-bit, and 64-bit. Therefore the system creates separate files to run everything smoothly without any conflict.
You won’t see any folder on a 32-bit variant of the Windows OS, which means you cannot install applications larger than 32-bit.
Why Is It Called Program Files (x86)?
You may wonder why Program Files are called Program Files (x86). The x in ‘x86’ refers to ISA (instruction set architecture).
This architecture has seen the following updates since it has been designed.
| Extension of x86 or 80×86 | |
| 16-bit instructions | 16-bit processors |
| 32-bit instructions | 32-bit processors |
When Intel first introduced 8086 architecture, it came with 16-bit instructions that could work for 16-bit processors. Then they extended it to 32-bit processors that work for 32-bit processors.
Formerly known as 80×86, this family of processors and instruction sets is referred to as x86.
With each extension, there has been more support for the features.
As you probably know, a 64-bit OS stores files and applications that are 32-bit in the ‘Program Files (x86)’ folder. 32-bit applications don’t store in the original folder ‘Program Files’ as the OS has another folder ‘Program Files (x86)’, where 32-bit applications are stored.
Furthermore, its emergence is from the 8086 processors and instructions set of Intel. Therefore, it is given the moniker x86.

What To Remove From Program Files?
You’re not required to delete anything in Program Files or Program Files (x86) unless you want to uninstall a program or application. Well, you shouldn’t mess up with the directory directly. You can choose the program or application and uninstall it by right-clicking on it.
Can You Delete Program Files?
It’s not a good idea to delete the ‘Program Files’ folders on the C drive. Nonetheless, if you still want to do so, it wouldn’t be an easy task.
First of all, you need to have admin access if it is not your computer. Then, deleting these folders will completely disturb the functioning of your Windows. The consequences of deleting these folders might result in reinstalling Windows.
Many people take this step when there is less space left on drive C. They either remove one folder from ‘Program Files’ or ‘Program Files (x86) or move them to a new drive.
When Should You Move Your Program Files From Drive C?
Before moving Program Files to another drive, make sure to keep a backup of Drive C in case Windows becomes irreparable.
Furthermore, you shouldn’t do this unless:
- Low space warning keeps popping up on your screen
- Your ‘Program Files’ and ‘Program Files (x86) are on SSD and SSD doesn’t have more space left
In any of the above scenarios, you can move these folders from drive C to another folder, though I still wouldn’t recommend deleting them.
If you don’t want to brick your system, the best alternative would be to move folders other than ‘Program Files’ and ‘Program Files (x86)’. For instance, you can make some space by moving ‘User folders’ to different drives. Also, you should consider doing this when you’ve just installed Windows.
What Is A Virus?
Since, we are on the topic of windows, knowing about viruses is a must.
The word “virus” refers to a program that reproduces itself independently and can spread from host to host. Viruses are also known as “malware” or “malicious software.”
A virus can affect any type of program file, including text, images, music, and video files too. In simple terms, a virus is a computer’s disease.

What Are The Effects Of Virus On Hard Drive Or C Drive?
The hard drive is exactly where your ‘Program Files’ reside. You’re probably wondering what kind of effects a virus can leave on a hard drive, which may further infect Program Files. In majority of the scenarios, the effects of viruses on your hard drive are not of such a serious nature that you can’t repair later.
Viruses are programs that attach to another program and damage it. A virus is a type of self-replicating program that infects other programs, usually by copying itself into them.
Here’s the list of viruses that can affect the Hard Drive or C Drive:
- Trojans
- Malware
- Rootkits
- Spyware
- Adware
- Worms
Running an infected program automatically activates the virus, which infects other programs as well. Additionally, you might lose the data saved on your hard drive.
You may also need an expert’s services in this regard. There are different severity levels of viruses; their effects can range from very subtle to malicious.

The following are the signs that indicate the presence of a virus in your C drive:
- Your computer slows down.
- Antivirus software sends notifications that there’s a virus.
- There’s zero storage on the hard drive.
- The computer starts behaving unusually.
- Applications start running and stopping on their own.
Conclusion
- In this article, you learned the difference between ‘Program Files’ and ‘Program Files (x86)’.
- Program files store 64-bit data, whereas Program Files (x86) store files and applications of 32-bit or less.
- You cannot move or delete these folders, or you may have to reinstall Windows.
Other Articles
- What’s The Difference Between A Minotaur And Centaur? (Some Examples)
- Attack vs. Sp. Attack in Pokémon Unite (What’s The Difference?)
- What Is The Difference Between Pathfinder and D&D? (Answered)
- The Difference Between Dorks, Nerds, and Geeks (Explained)